Introduction
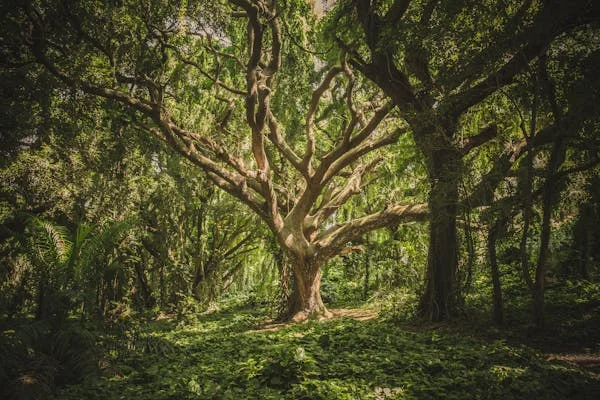
Lesy AD is a term that originates from the deep-rooted Slavic traditions, referring to forests as vital ecosystems that intertwine with natural and cultural significance. In the Slavic context, the term “Lesy” translates to “forests,” representing not just physical wooded areas, but a domain rich in biological diversity, cultural symbolism, and ecological importance. The “AD” suffix further highlights the dynamic relationship between these forests and the various species within, particularly focusing on spiders. Through exploring this unique term, we uncover how forest ecosystems function and how species like spiders contribute to maintaining a delicate ecological balance.
In this article, we’ll delve into the ecological, cultural, and biological importance of Lesy AD, exploring how these forests impact human life, biodiversity, and conservation efforts in a changing world.
Its Ecological Importance
At its core, Lesy AD stands as a representation of the forests, often intertwined with spiritual, cultural, and biological importance in Eastern European societies. These forests, a prominent part of Slavic heritage, hold more than just trees; they are home to a variety of life forms that coexist in delicate balance. When we consider the environmental framework of Lesy AD, the role of spiders emerges as central to maintaining ecological health.
Forests are much more than simple green spaces; they are hubs of biodiversity, water purification, carbon sequestration, and habitat for a wide range of species. From an ecological standpoint, Lesy AD emphasizes the vital role of these ecosystems in supporting both plant and animal life. These spaces represent the intricate web of life that spans from towering trees to the smallest arachnids. In particular, spiders, through their web-building and hunting habits, contribute significantly to pest control and, by extension, the balance of the ecosystem.
The Deep Cultural Significance of Forests in Slavic Traditions
The reverence for forests in Slavic culture is profound. Lesy or “the forest” is not merely a physical space but a sacred entity that serves as a refuge for the spirit and life itself. For centuries, these forests have inspired countless legends, and their presence in Slavic mythology is intertwined with themes of life, death, and the unseen world.
Forests have been seen as the boundary between the known world and the mystical realm. In some legends, the forest is inhabited by mythical beings spirits that protect and guard the trees, creatures, and resources. They are seen as a mirror of human nature: unpredictable, wild, but ultimately necessary for the balance of life.
Key Cultural Insights on Forests:
- Spiritual significance: Forests are often seen as realms of mystery, housing both divine and malevolent spirits in Slavic folklore.
- A Source of Life: Historically, forests were the primary source of resources, from food to timber, and also places of spiritual and mystical experiences.
- Symbolism of Connection: Forests in folklore symbolize the interconnection of life, much like the interconnected web of nature.
These beliefs highlight why maintaining the health of forests, such as those described in Lesy AD, is not only a matter of ecology but also a matter of cultural preservation.
Spiders: Unsung Heroes of Forest Ecosystems
While spiders may not be the first species that come to mind when considering the importance of forests, they play an integral role in their maintenance. Spiders are pivotal in controlling insect populations, which, if left unchecked, could wreak havoc on plant life and the overall biodiversity of a forest.
The webs that spiders construct are more than just tools for trapping prey; they are also indicators of the health of the ecosystem. A strong, thriving spider population often indicates a healthy forest. Conversely, a drop in spider numbers can signal the onset of environmental stress, such as pollution, climate change, or habitat destruction.
Key Contributions of Spiders:
- Insect Control: Spiders help control insect populations by trapping flying and crawling insects, preventing the overgrowth of pest species that might otherwise damage plants.
- Recycling Nutrients: When spiders catch prey, they contribute to the nutrient cycling of the ecosystem. Their waste products break down into organic matter that nourishes the soil.
- Food Source: Spiders are an essential food source for many animals, including birds, lizards, and small mammals, supporting higher levels of the food chain.
Their webs, which vary in design and purpose, serve as both a tool for survival and a symbol of the complexity of forest ecosystems.
Biodiversity in Forests: The Role of Webs and Insect Control
One of the fundamental features of Lesy AD forests is biodiversity. Biodiversity in forest ecosystems includes all forms of life from plants and fungi to insects and arachnids. Spiders, in particular, contribute to the biodiversity of these environments by forming webs that capture insects, which would otherwise overpopulate and destabilize the ecosystem.
Each spider species is adapted to a different ecological niche, and their webs reflect this diversity. Some spiders build orb-shaped webs to catch flying insects, while others weave tangled webs for crawling prey. The diversity of webs within a forest adds structural complexity, providing homes and hunting grounds for a wide range of species.
Example of Different Spider Webs:
| Spider Web Type | Spider Species | Main Purpose |
| Orb Webs | Orb-Weaving Spiders | Trap flying insects |
| Funnel Webs | Funnel-web Spiders | Capture prey that enters the funnel |
| Cobwebs | Tangle-web Spiders | Trap crawling insects and small prey |
Each web design serves a specific ecological purpose, contributing to the forest’s biodiversity by supporting different animal and insect populations.
How Forests and Spiders Rely on Each Other
The relationship between forests and spiders is one of mutual benefit. Forests provide the habitat and resources spiders need to survive, while spiders help keep the ecosystem in balance by controlling insect populations. This interdependency highlights the complex web of life in forests like Lesy AD, where every species, no matter how small, plays a vital role.
Spiders help keep forest ecosystems healthy by reducing the number of insects that could otherwise destroy plant life, and in turn, their webs serve as vital markers of the health of the forest. A change in spider populations whether through loss of habitat or a change in environmental conditions can signal larger changes in forest health.
Conservation and Preservation of Forests and Spiders
As ecosystems face increasing threats from deforestation, climate change, and pollution, it becomes essential to preserve both forests and the species that inhabit them, including spiders. Lesy AD serves as a reminder of the need for concerted efforts to protect these natural spaces.
Key conservation strategies include:
- Forest Protection: Safeguarding forests from logging, urbanization, and unsustainable agriculture practices.
- Pollution Control: Reducing chemical use and industrial pollutants that harm spider populations and disrupt forest ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Protecting the full range of species within forests to ensure that ecological functions, such as pest control and pollination, continue uninterrupted.
Lesy AD in Slavic Folklore and Mythology
In Slavic folklore, forests hold a mystical significance, often seen as the home of spirits, gods, and mythical creatures. The relationship between humans and forests is one of both reverence and fear. The Lesy AD concept ties into these traditions, where forests are seen as places that contain both life and danger.
Spiders also appear in folklore, often symbolizing fate, destiny, and the interconnectedness of life. The idea of the “web of life” is closely related to the spider’s role in these stories, where every strand of the web is a representation of a different thread of existence.
Challenges Facing Forests and Their Inhabitants
Despite their importance, forests face significant challenges that threaten their survival. Climate change, pollution, and deforestation are among the leading causes of ecosystem degradation. The impact of these threats is felt not only by trees but also by the countless species that depend on them, including spiders.
Key Threats to Forests:
- Deforestation: Rapid loss of forested areas due to logging and urban expansion.
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature and weather patterns disrupt the balance of species within forests.
- Pollution: Industrial runoff and chemical pollutants harm soil quality, water resources, and biodiversity.
Solutions: How to Protect and Revive Forest Ecosystems
To address these challenges, we must focus on sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and local communities. Strategies for protecting Lesy AD and ensuring the health of forests include:
- Reforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas to restore habitats.
- Sustainable Forest Management: Implementing practices that allow for the use of forest resources without compromising their health.
Conclusion:
Lesy AD, the symbolic representation of forests in Eastern Europe, plays a critical role in maintaining biodiversity, cultural heritage, and ecological health. The interconnectedness of forests, including the spiders that inhabit them, forms a complex but essential balance. These ecosystems are not only critical for the survival of countless species, but they also provide essential services to human communities, including air purification, water regulation, and climate control.
Through efforts to preserve and protect Lesy AD, we ensure that forests and the species within, like spiders, continue to thrive. Their importance goes beyond mere survival; they are the heartbeats of ecosystems, cultures, and spiritual traditions.
As we face the challenges of climate change, habitat destruction, and environmental degradation, it becomes more critical than ever to adopt sustainable practices. By working to conserve forests and protect the delicate webs that sustain life within, we ensure that future generations can benefit from the beauty, diversity, and stability that these ecosystems provide. The health of our forests and the species they support, like the humble spider, are key to preserving the balance of life on Earth.
FAQs about Lesy AD
What does Lesy AD mean?
Lesy AD refers to the term “forests” in Slavic languages, emphasizing their ecological and cultural importance. The “AD” adds a modern ecological perspective, highlighting the interplay between forests and biodiversity.
Why are forests important in ecosystems?
Forests provide essential services like air purification, carbon storage, water regulation, and biodiversity support. They are vital for maintaining ecological balance and sustaining numerous plant and animal species.
What role do spiders play in forest ecosystems?
Spiders are natural pest controllers in forests. They manage insect populations, contribute to nutrient cycling. They act as prey for larger species, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance.
How does Lesy AD connect to Slavic culture?
In Slavic culture, forests symbolize mystery, life, and spirituality. They are often depicted in folklore as sacred spaces, highlighting their cultural and ecological significance.
What are the main threats to forests like Lesy AD?
The major threats include deforestation, climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. These issues disrupt biodiversity and weaken the ecosystem services forests provide.
How can we protect and conserve forests?
Conservation strategies include reforestation, sustainable forest management, reducing deforestation, pollution control, and engaging local communities in preservation efforts. Protecting biodiversity, including species like spiders, is essential for a balanced ecosystem.